Characteristic strength of concrete is one of the important properties of concrete which indeed unanimously by design engineeror any other person involved in the construction sector.
The compressive strength of concrete is given in terms of the characteristic compressive strength of 150 mm size cubes tested at 28 days (fck)- as per Indian Standards (ACI standards use cylinder of diameter 150 mm and height 300 mm). The characteristic strength is defined as the strength of the concrete below which not more than 5% of the test results are expected to fall.
This concept assumes a normal distribution of the strengths of the samples of concrete.
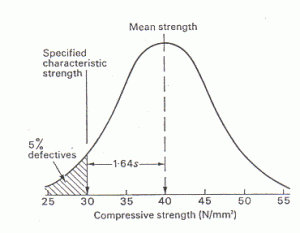
Normal Distribution curve on test specimens for determining compressive strength
The above sketch shows an idealized distribution of the values of compressive strength for a certain number of test specimens. The horizontal axis represents the values of compressive strength in MPa. The vertical axis represents the number of test samples for a
particular compressive strength. This is also termed as frequency.
The average of the values of compressive strength (mean strength) from the graph is 40 MPa. The characteristic strength (fck) is the value in the x-axis below which 5% of the total area under the curve falls. From the graph we can clearly say that 30 MPa is the characteristic strength of the given concrete mix. The value of fck is lower than fcm (40 MPa- mean strength) by 1.64σ, where σ is the standard deviation of the normal distribution.
So we can say the given concrete mix has a characteristic strength of 30 MPa or it is a M30 grade mix.
M- Mix
* Note: For a 95% confidence level k=1.64 , hence k value varies on the confidence level of the experiment
Definition:
Characteristic strength of concrete is the strength of concrete specimens casted and tested as per given code of practice and cured for a period of 28 days; 95% of tested cubes should not have a value less than this value.
